Using bacteriophages to combat antimicrobial resistance
Using Bacteriophages to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
Breaking News, Daily Updates & Exclusive Stories - asarkari
In an unprecedented battle against antimicrobial resistance (AMR), scientists are turning their attention to bacteriophages, natural viruses that specifically target and kill bacteria. As antibiotic resistance continues to rise globally, effective treatments are rapidly dwindling. This new approach, leveraging the ability of phages to evolve alongside bacteria, could turn the tide in the fight against resistant infections.
Understanding Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them. In simpler terms, the more we use antibiotics, the more we create a resistant strain of bacteria. As a result, infections that were once easily treatable have become significantly harder to manage, leading to longer hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality.
The Role of Bacteriophages
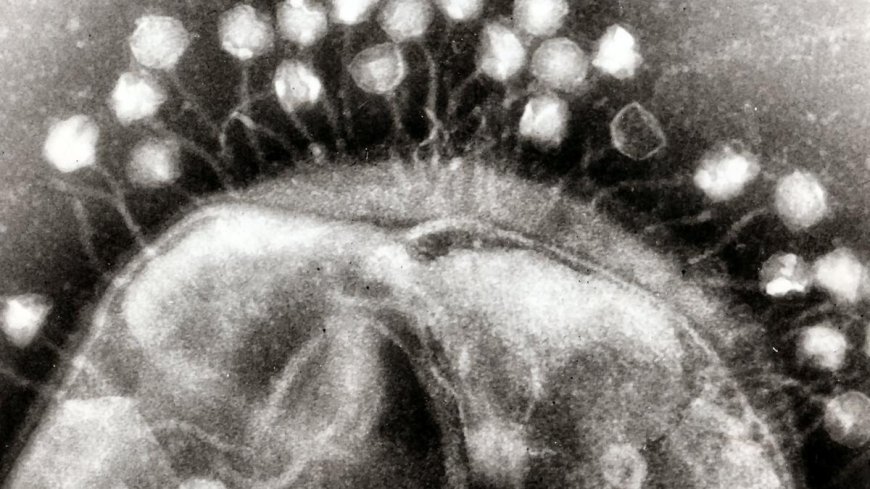
Bacteriophages, or phages for short, are a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics. These viruses, which exclusively infect bacteria, can rapidly replicate and adapt to the evolving defenses of their bacterial hosts. While bacteria may evolve to evade a phage’s attack, research indicates that phages can also develop strategies to circumvent bacterial resistance mechanisms. This dynamic interplay is what makes phage therapy an attractive solution in the fight against AMR.
Recent Research and Developments
Recent studies have highlighted the potential of phage therapy as both a treatment and a preventive measure. A groundbreaking study from scientists at the Indian Institute of Technology demonstrated induced phage resistance in specific bacterial strains. This study revealed that by using a combination of multiple phages, the chances of bacterial resistance can be significantly reduced. Moreover, continued research is being conducted to map out the phage genomes, which can provide insights into how they can be utilized against specific bacterial infections effectively.
Expert Commentary on Phage Therapy
Dr. Anjali Sharma, a leading microbiologist, remarked, "The future of combating bacterial infections lies in harnessing the natural enemies of bacteria: phages. Unlike antibiotics, which indiscriminately kill both good and bad bacteria, phages target only pathogenic strains, which makes them a more precise treatment option." This precision could revolutionize how we approach infections that have become resistant to treatment.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the promising benefits of phage therapy, challenges remain. Regulatory hurdles, the need for personalized treatments based on individual bacterial profiles, and public acceptance pose significant challenges in the widespread adoption of this therapy. Nonetheless, as research continues, stakeholder engagement and collaboration among researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers will be crucial in overcoming these obstacles.
Conclusion
In the midst of a rising tide of antimicrobial resistance, bacteriophages offer a glimmer of hope. Their ability to evolve and combat resistant bacteria presents a novel approach that could potentially save countless lives in the coming years. As we advance in our understanding and application of phage therapy, it might just redefine the future of infectious disease treatment. For more updates, visit https://asarkari.com.
Keywords:
bacteriophages, antimicrobial resistance, phage therapy, antibiotic resistance, bacterial infections, natural viruses, healthcare innovations, medical research, infectious disease treatment.What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0









































